Although Geocells may Look the Same, their Material Composition Determines Performance
Required properties and performance are described by ISO, ASTM and other standards for geocell reinforcement
While geocells may appear similar, their material composition significantly impacts their long-term performance. This page highlights the critical properties that determine a geocell’s durability and suitability for specific applications.
Understanding Geocell Performance
The performance of geocells in reinforced road pavements and other long-term applications is measured by ISO, ASTM and other standards. For example, creep, the tendency of polymeric materials to elongate over time, and loss of elastic modulus can lead to dimensional instability and loss of confinement, ultimately compromising the structural integrity of the project. The choice of polymer composition plays a pivotal role in geocell performance.
Contact Us to help you choose the right geocell for your project
Four Critical Factors for Geocell Durability
- Dynamic Mechanical Modulus (Elastic Stiffness)
- Permanent Deformation (Creep)
- Cell Tensile Strength
- Environmental Durability
The choice of geocell material properties directly influences the project’s design, performance, and design life. For example, a geocell with superior creep resistance can withstand higher loads and maintain its confinement for longer periods. Similarly, a geocell with a high dynamic modulus can resist long-term cyclical loading from high traffic conditions.
Detailed Analysis
-
- Dynamic Mechanical Modulus (Elastic Stiffness). DMA test (ISO 6721-1, ASTM E2254) measures the geocell’s ability to store and release dynamic loading while maintaining its shape. A geocell with superior elastic stiffness provides better confinement and reduces the risk of structural failure. Read more
- Permanent Deformation (Creep). SIM test (ASTM D-6992) predicts the geocell material’s permanent deformation under specific loads and temperatures. Geocells with low creep resistance may lose their shape and confinement, leading to reduced performance and potential failure. Read more
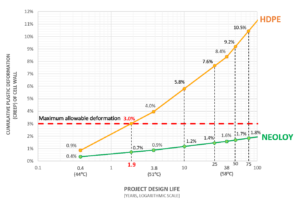
Based on research with leading research institutes, plastic deformation (volumetric expansion) of the geocell strip above 3% will impact confinement: lower compaction density, increase settlement and increase the chance of failure.
- Cell Tensile Strength. The strip tensile strength test (ISO 10319:2015) determines the ability of a geocell to withstand vertical and horizontal loads. A geocell with high tensile (hoop and weld) strength can better resist deformation and maintain its integrity under heavy loads. Read more
- Environmental Durability. HPOIT test (ASTM D5885) assesses the geocell stability (resistance) to environmental factors such as UV radiation, heat and oxidation. A geocell with high environmental durability maintains its performance properties over a longer lifespan. Read more
Choosing the Right Geocell
The influence of geocell properties on the design and performance are key considerations in ensuring long-term success. While geocells may appear similar, their material properties and performance characteristics can vary significantly. By understanding these critical factors and the advantages of Novel Polymer Alloys (NPA), engineers can select rigid geocells with performance criteria that meet international standards and the requirements of their projects. Contact us for expert guidance in choosing the ideal geocell solution.
- Manufactured from NPA – Neoloy Polymeric Alloy
- High tensile strength (Tensile test >19 kN/m) and dynamic stiffness (DMA test >500 MPa)
- Excellent resistance to permanent deformation (SIM test <2% over project design life)
- Superior long-term durability (HPOIT test >1600 min)
- Meets or exceeds ISO, ASTM and other standards for geocell reinforcement
Comparison of HDPE Soft-Cells vs Neoloy Tough-Cells:
| Material Properties Criteria |
Soft-Cells (HDPE)* |
Tough-Cells (Neoloy) | ||||
| Elastic Stiffness (DMA test) | X | Low | V | High 2x | ||
| Creep Resistance (SIM Test) | X | Very Low | V | Very high 20x | ||
| Tensile Strength (Tensile test) | X | Low | V | High 7x | ||
| Environmental Durability (HPOIT test) | X | Low | V | Very high 5x | ||
Read More About Choosing the Right Geocell
Choosing Neoloy Tough Cells for High Performance Infrastructure – Pioneering Geocell Technology for Soil Stabilization and Road Reinforcement in Civil Engineering
Neoloy® NPA – Novel Polymeric Alloy for Strong & Stiff Geocells – The NPA material in the PRS Neoloy Tough-Cells enables a new generation of geocell, with performance properties guaranteed for the project design life.
Neoloy based Tough-Cells vs HDPE Soft-Cells – Compared to HDPE Soft-Cells, Neoloy Tough-Cells maintain greater stiffness, bearing capacity and stress distribution, while reducing deformation.